
Home List your patent My account Help Support us
GRAPHENE-BASED DRUG DELIVERY DEVICE FOR MUCOSAL ADMINISTRATION
[Category : - HEALTH]
[Viewed 800 times]
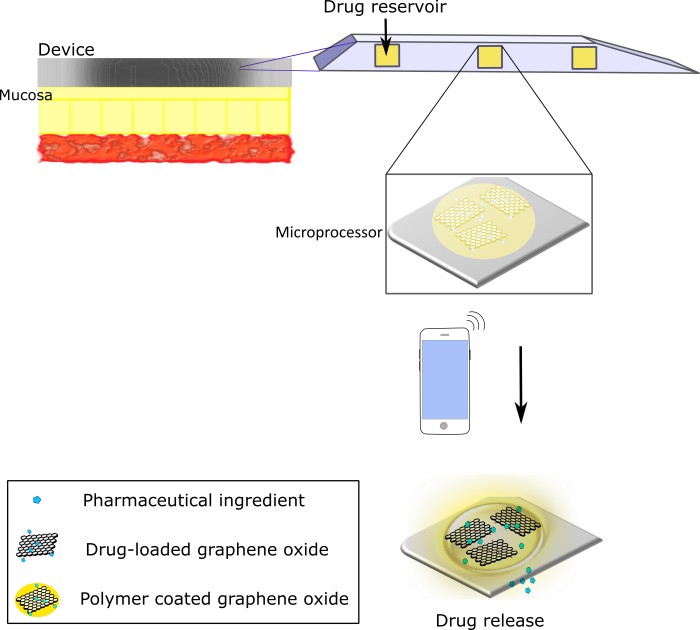
The present invention proposes a removable drug delivery system combining the drug-delivery operation principle applied to mucosa drug-release from multiple reservoirs. rnThis invention takes advantage of the electrical conductivity properties of graphene and of its great potential to operate as a drug- and electron-carrier to create a programmable drug delivery. These properties provide a miniaturized tunable drug-delivery system, capable of finely regulating rate, timing and speed of drug release. rnThe role of graphene as drug carrier for drug delivery system has been widely explored in the past: the present device is capable of a controlled retainment and release of drugs for extended periods of time, as well as of an immediate release for quick action of drugs at different doses on an as-needed basis. rnThe present innovation combines immediate-release system and zero-order release system improving pharmacokinetics of mucosa drug release.
POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS:
Properly loaded, the device may be applied for the therapeutic treatment of gastrointestinal, genitourinary and psychiatric disorder, neurological disorder and nutritional deficiency, including but not limited to adrenal insufficiency, allergy, anxiety disorder, asthma, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, bipolar disorder, chronic and acute pain, chronic bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, congestion, cramp, cyclic vomiting syndrome, dementias, dependence syndrome, diabetes mellitus, epilepsy, fever, genitourinary disorder, hypercholesterolemia, hormonal imbalance, hyperglycaemia, hypersalivation, hypertension, hypotension, hypothyroidism, infectious disease, inflammatory diseases, menopause, menstrual regulation, migraine, mood disorders, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, neoplasms, obesity, Parkinson's disease, pulmonary disease, respiratory disease, sexual dysfunction, sleep disorder, smoking cessation, vaginal diseases, vomiting.
ADVANTAGES AND INNOVATIONS:
• Drug release period: it has been previously proposed a drug delivery device with either one-time release (i.e. for an acute treatment) or long-term operation (i.e. for chronic treatments, over 2-12 months). We are instead proposing a tunable drug-delivery system for both short- and long-term release profiles, even altering drug release schedule in real-time, constantly operating on a time-scale of a few minutes to hours.
• Drug release stimuli: the use of electrical stimuli was previously proposed to actuate the drug reservoirs, in passive release or ion-responsive drug release systems. Somewhat similar, we are proposing electrical-, light- and magnetic-induced drug-release exploiting graphene properties and inducing an active compound release thanks to its drug- and electron-carrier properties. In this sense, electrical stimuli may modulate graphene’s ability to establish a balance between physicochemical properties of graphene and bioavailability of drugs. For instance, the amount of drug released at mucosa/submucosa level depend on the graphene electrical conductivity property, allowing on-demand release of drugs be controlled by the smartphone app.
• Pharmaceutical compounds: previous proposals included reservoirs suitable for either one single or several drugs storage. However, in those devices the release actuation cannot be specified independently for each drug. We are instead proposing a drug reservoir suitable for either one single or several drugs, with various dosage. The properties of graphene as a drug-carrier system offer the peculiar ability to conjugate different drugs in a single graphene sheet, promoting a synergy and versatility of operation controlling additive effects of distinct pharmaceutical compounds.
• Vehicle formulations properties: most of commercial transmucosal pharmaceutical formulations contains polymer composites that play an important role as a vehicle in the drug-delivery formulations, by providing controlled release of pharmacologic agents. However, due to its high density the availability of the drug for immediate release to the mucosal membranes progresses slowly. Graphene can instead overcome this problem and immediately deliver the drugs, requiring a reduced amount of polymer or even completely replacing it in the pharmaceutical formulation. Moreover, due to graphene electrical and nanocarriers properties, the electrical currents generated by the microprocessor may break ionic bonds of the drug-conjugated graphene compound, promptly releasing the drug and expelling it out of the reservoir, thus enhancing in situ availability.
Asking price:
Make an offer
Make an offer
[ Home | List a patent | Manage your account | F.A.Q.|Terms of use | Contact us]
Copyright PatentAuction.com 2004-2017
Page created at 2025-12-29 13:41:52, Patent Auction Time.
 Patent publications:
Patent publications: WO 2023174910
WO 2023174910 Great invention
Great invention